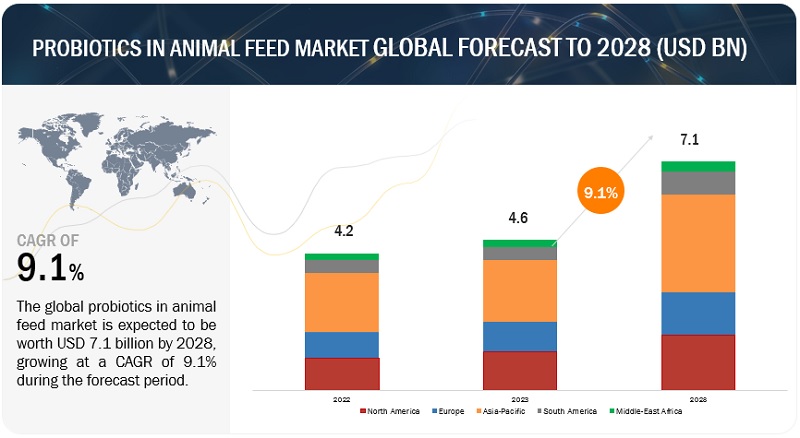
The global probiotics in animal feed market is projected to reach USD 7.1 billion by 2028 from USD 4.6 billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 9.1% during the forecast period in terms of value. Owing to the increase in production and demand of compound feed along with rising consumption of feed additives in emerging markets such as Asia Pacific and South America.
Download PDF Brochure:
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=85832335
Pressure on feed productivity and feed conversion rate to drive the demand for probiotics in animal feed market
Feed conversion rate/ratio can be defined as, efficiency with which the bodies of livestock convert animal feed in the desired output. With a significantly high demand for livestock products, there has been increasing pressure on the livestock sector to meet the growing demand for high-value animal protein. This has subsequently increased the livestock population, which has resulted in increased consumption of probiotics in feed as they optimize the nutritional value of feed. The probiotics act as bactericidal and thus helps in further enhancing the performance of livestock by improving gut health and acting as a growth promoter. Therefore, feed incorporated with probiotics helps increase the feed conversion rate/ratio thereby catering to the demand.
Probiotics in animal feed act as an important aid to improve livestock health and production while improving digestion and feed efficiency. Thus, increased pressure on feed productivity and high demand for faster feed conversion rate is fueling the market for probiotics in animal feed.
Increased prevalence of disease outbreaks to augment the market growth
Unsafe and adulterated feed ingredients reduce the immunity of animals, thereby causing productivity loss by affecting the quality of animal products. The increased prevalence of disease outbreaks has encouraged livestock farmers to purchase superior-quality feed products with additives. Safety and quality of products have always been a high priority for customers, as disease outbreaks can affect the production, trade, and consumption of livestock products, such as dairy products, meat, egg, and other by-products. Furthermore, regions affected by such outbreaks are banned from exporting products for a prolonged period until completely quarantined and controlled. In the recent past, the Asia Pacific region experienced outbreaks of SARA-CoV-2 virus (2019), H5N1 influenza virus (2014) and foot-and-mouth disease (2011), which impacted trade, and livestock producers incurred heavy losses due to increased awareness about animal welfare.
Request Sample Pages:
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=85832335
Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period
Countries such as China, India, Japan, Australia & New Zealand, and rest of the Asia Pacific have been considered in this study. Some of the factors for the high demand of the market in Asia Pacific region includes growing population, rise in disposable incomes, and rapid urbanization. Increasing demand for meat and animal products among the growing population of the Asia Pacific region along with the rising affluence in the region resulted in high consumption of meat products. This has also resulted in intensified livestock production for meat, which in turn drives the need for improved animal health and performance.
The growth of the meat industry in developing economies such as India and China, as well as the increased consumption of quality meat products, are primary drivers for the Asian market. Augmented concern over livestock diseases and outbreaks of infections has further highlighted the importance of animal health and wellness to ensure the safety of end users. The advent of globalization and urbanization has caused a shift in consumer preferences, where consumers opt for nutritious, quality food products and like to experiment with food choices. These factors are expected to continue in the coming years, driving demand the for probiotics in animal feed market.
No comments:
Post a Comment